The Way Currency Exchange Rates Work
p{text-align: justify;}td p{text-align: center;}
The currency exchange rate is the cost of exchanging one currency for another. They usually reflect the relative strength of the two economies and currencies. The US dollar will typically gain strength against other currencies, for instance, if the US economy is strong. This means purchasing one US dollar will require more than those other currencies. On the other hand, the US dollar will lose value relative to other currencies if the US economy is struggling. This means that compared to those other currencies, buying one US dollar will cost less.
Forex traders set the exchange rates for most currencies. The currency exchange market is open all day long, all week long.
What is a currency exchange rate?
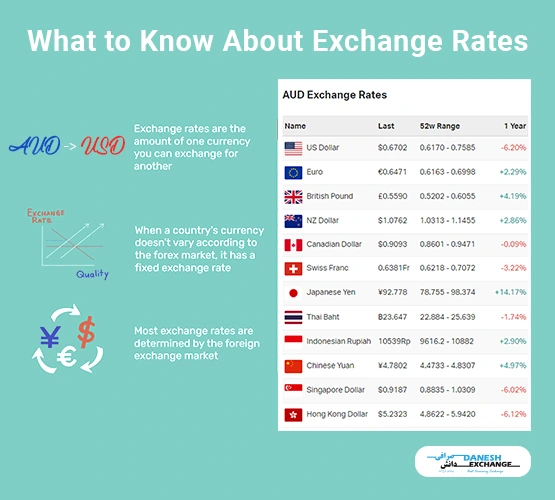
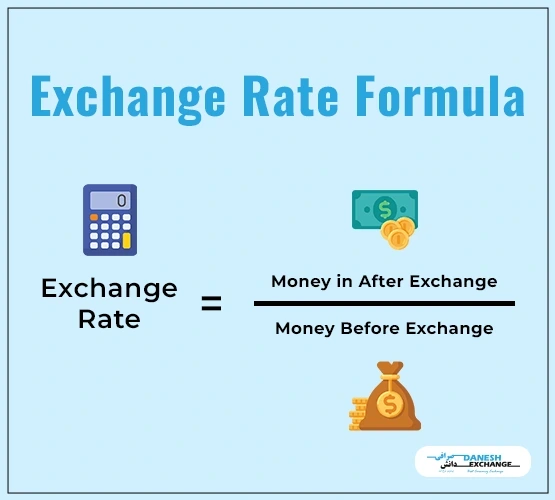
The value difference between two currencies, like the Australian and US Dollar, is known as an exchange rate. For example, The way currency exchange rates work is if you want to exchange Australian dollars for US dollars, you would take your Australian dollars (or bank card) to the currency exchange shop and use them to purchase US dollars. The international spot rate would determine the amount you could buy, a price decided by a daily currency trading network of banks.
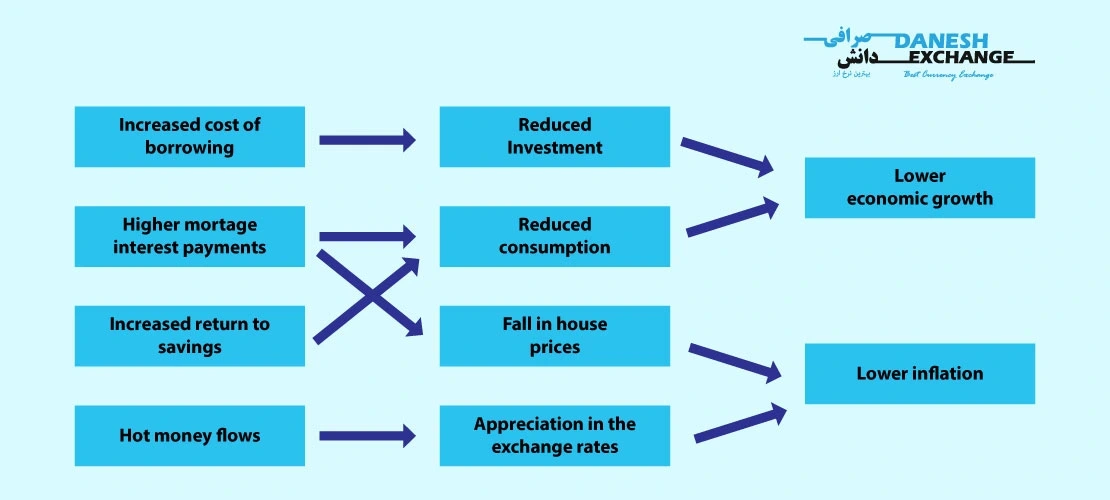
Factors that affect foreign exchange ratesInflation |
Important takeaways
- Businesses that offer currency exchange services let customers trade one currency for another.
- Some countries’ exchange rates are constantly fluctuating, while others have a fixed exchange rate.
- Currency exchanges are available in physical locations such as banks and airports, but they are also becoming more common online.
- Currency exchange fees vary so greatly that credit card fees may be lower than those paid using adjusted exchange rates.
- The currency rate is affected by the viewpoints of an economy and society.
Currency Exchange rates are divided into two categories
Flexible – Flexible exchange rates change often.
Fixed – Fixed exchange rates change rarely.
Flexible: The foreign currency exchange market determines the majority of exchange prices. As a result, exchange rates vary from moment to moment. These are Called Flexible.
Prices are always changing for the currencies that Americans most often use. Some currencies like Mexican pesos, Canadian dollars, euros, etc. are among them. The government and central bank do not intervene with currency exchange rate maintenance. Government policies may have a long-term effect on currency rates, although, in most situations, they can only affect rather than regulate them.
Fixed: Other currencies, such as the Saudi Arabian riyal, shift rarely. That’s because fixed currency exchange rates are used in certain nations, and they do only later when the government says so. These rates are usually connected to the US dollar. Their central banks have sufficient foreign currency reserves to manage the value of their currencies.
Why is the currency falling in value?
The value of each unit of currency decreases when economic growth falls more quickly than the coin’s value. Inflation, the most common monetary phenomenon, is caused by the opposite process: money accumulation grows faster than productivity.
Exchange rates can be challenging to understand, but we can assist. Here are four guidelines to remember when exchanging rates:
- Pay attention to the news. Exchange rates are greatly influenced by economic news.
- Consider your country’s currency. If you need to exchange it for another currency, you might be able to get a better rate.
- Keep in mind the costs. Ask about any possible fees when you receive an exchange rate quote.
- Examine prices. Comparing prices can help you get the best deal.
Also, you can visit our page Foreign exchange rates for more information about updated currency rate.
The Location of Exchange Currency
If you are looking for Currency Exchanges services, you can easily find them in Australia. Put your faith in Danesh exchange for the lowest possible rate with no hidden fees. You can also receive your currency anywhere, whether online or in-store.
Additionally, there are other ways to exchange money, including at hotels, airport kiosks, and overseas banks.
Understanding the currency rate might look complicated, but you’ll get it soon when you concentrate on this topic. It’s a crucial topic these days. So you should keep yourself updated with the daily foreign currency exchange rate.



 May 25, 2022
May 25, 2022  3 Min Read
3 Min Read